Abstract
- Why should we consider using Vcluster? Our requirement is to establish multiple environments for developers to facilitate development, testing, as well as regression and performance tests.
- The crucial aspect is ensuring that these environments closely mimic the structure of our staging and production environments, which are based on Kubernetes. Instead of relying on Kubernetes namespaces to create these environments, We opt to offer developers a solution that provides them with an environment that closely resembles a real Kubernetes cluster. This is where Vcluster comes into play.
- Watch Demo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vWNkGyLajJE
- Source code: https://github.com/vumdao/multi-tenancy-using-vcluster-in-eks/tree/master
Table Of Contents
Open Table Of Contents
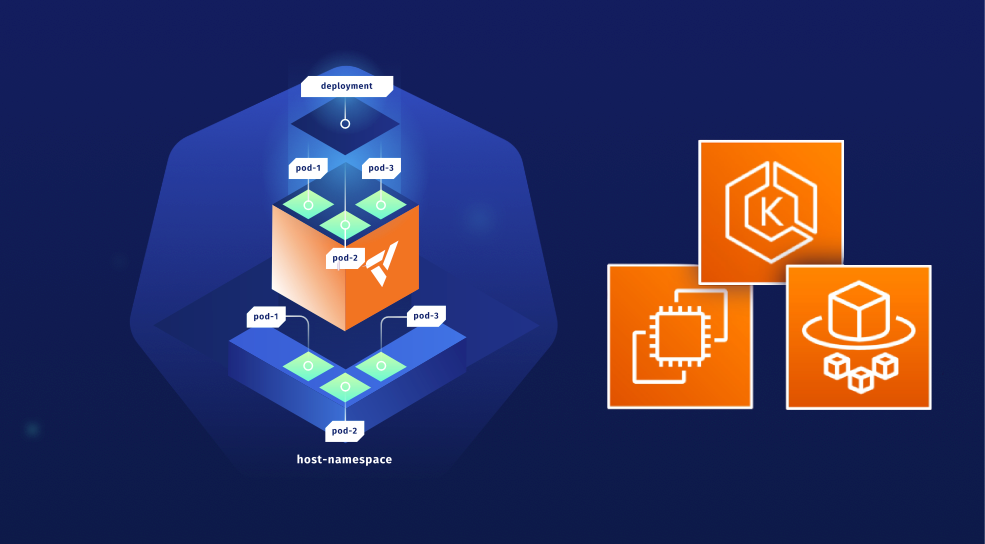
🚀 vcluster overview
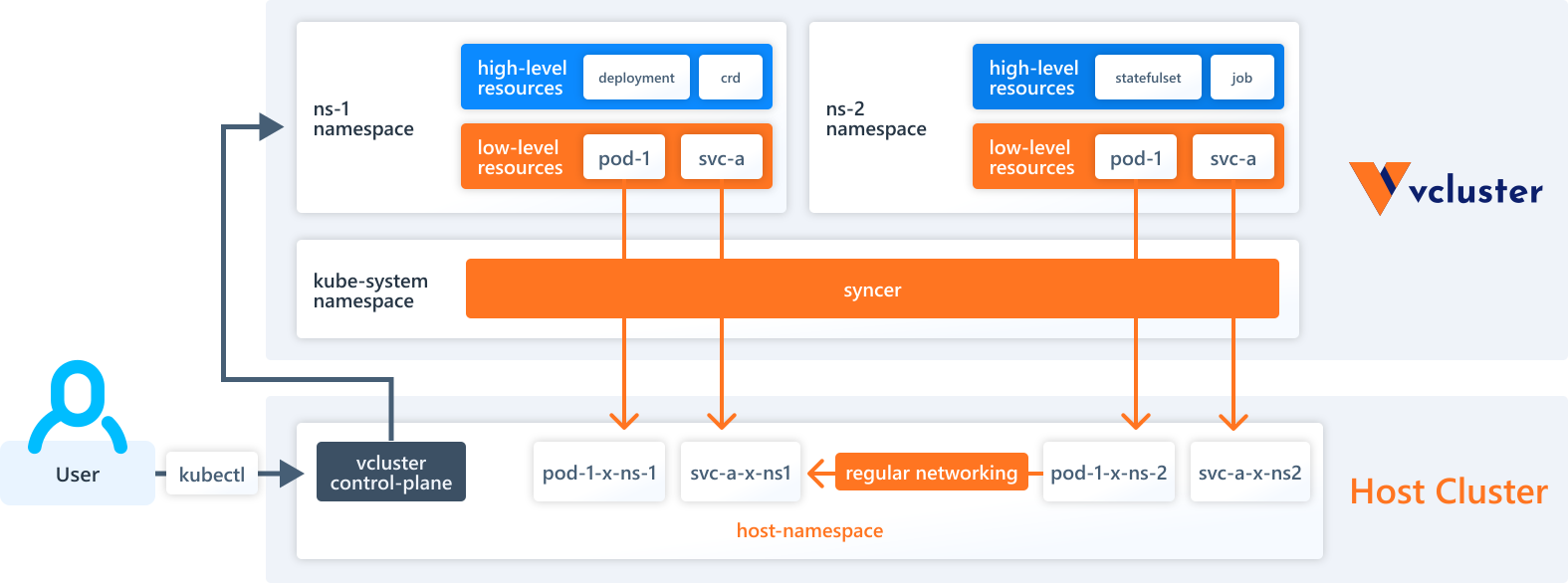
🚀 Solution overview
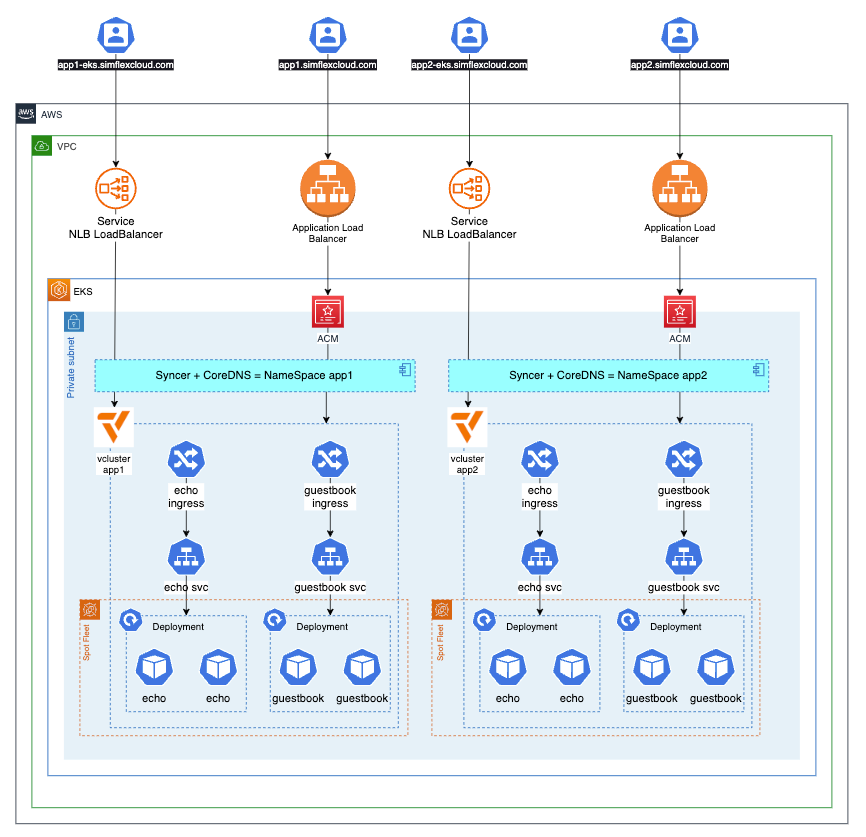
🚀 Bootstrap EKS cluster using CDK EKS Blueprints
-
The bootstrap provisions EKS cluster with required AddOns using CDK EKS blueprints
new VpcCniAddOn(), new MetricsServerAddOn(), new KarpenterAddOn(), new AwsLoadBalancerControllerAddOn(), new EbsCsiDriverAddOn(), -
Cluster provider
- Fargate to deploy Karpenter
- Karpenter simplifies Kubernetes infrastructure with the right nodes at the right time.
🚀 Create vcluster
- Create two vclusters with namepsace
app1andapp2$ ./demo/create-vcl.sh app1 $ ./demo/create-vcl.sh app2
🚀 Expose vcluster using Network Laoad Balancer
-
Create NLB service
✗ k apply -f demo/app1/service.yaml service/app1-lb created ✗ k apply -f demo/app2/service.yaml service/app2-lb created ✗ k get svc -n app1 app1-lb NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE app1-lb LoadBalancer 172.20.150.105 k8s-app1-app1lb-bb32c11098-3381306256798df4.elb.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com 443:32392/TCP 30h ✗ k get svc -n app2 app2-lb NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE app2-lb LoadBalancer 172.20.78.127 k8s-app2-app2lb-4690ffbcfe-bfb88a1245728e8a.elb.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com 443:31510/TCP 49s -
Create CName record point to the NLB DNS
➜ multi-tenancy-in-eks-using-vcluster git:(master) ✗ ./demo/r53-record.sh create app2 ➜ multi-tenancy-in-eks-using-vcluster git:(master) ✗ ping app2-eks.simflexcloud.com PING k8s-app2-app2lb-4690ffbcfe-bfb88a1245728e8a.elb.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com (13.250.162.120): 56 data bytes -
Now we can connect to the vcluster app1 and app2 using their expose endpoint
-
https://app2-eks.simflexcloud.com
✗ vcluster connect app2 -n app2 --server=https://app2-eks.simflexcloud.com --update-current=false done √ Virtual cluster kube config written to: ./kubeconfig.yaml - Use `kubectl --kubeconfig ./kubeconfig.yaml get namespaces` to access the vcluster
🚀 Deploy applications on vcluster
-
Deploy
echoandguestbookproject✗ ka2 apply -f demo/app2/vcluster ingress.networking.k8s.io/echo created deployment.apps/echo created service/echo created ingress.networking.k8s.io/guestbook created service/redis-leader created deployment.apps/redis-leader created service/redis-follower created deployment.apps/redis-follower created service/frontend created deployment.apps/frontend created -
Get ALB DNS and point to the Web app endpoint
-
✗ ka2 get ingress NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE echo alb * k8s-app2-dbb948e3be-939359744.ap-southeast-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80 10s guestbook alb * k8s-app2-dbb948e3be-939359744.ap-southeast-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80 10s ✗ ./demo/r53-record.sh create app2 k8s-app2-dbb948e3be-939359744.ap-southeast-1.elb.amazonaws.com
🚀 Cleanup
-
Delete vcluster
✗ vcluster delete dev -n dev info Delete vcluster dev... done √ Successfully deleted virtual cluster dev in namespace dev done √ Successfully deleted virtual cluster pvc data-dev-0 in namespace dev -
Destroy all AWS resources within this project